Saccharin Insoluble USP NF BP Ph Eur FCC Food Grade & Saccharin Sodium Suppliers Exporters, Manufacturers
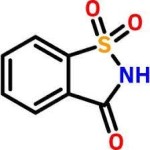
Saccharin Insoluble
CAS Number: 81-07-2 USP NF BP Ph Eur FCC Food Grade Suppliers Exporters, Manufacturers

Please visit Safety Data Sheet of Saccharin Insoluble USP NF BP Ph Eur FCC Food Grade Manufacturers.
Saccharin USP NF Grade Specifications:
C7H5NO3S --- 183.18
1,2-Benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one, 1,1-dioxide;
1,2-Benzisothiazolin-3-one 1,1-dioxide CAS 81-07-2
DEFINITION
Saccharin contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of saccharin (C7H5NO3S), calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared Absorption.
ASSAY
Procedure
Sample: 500 mg
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in 40 mL of alcohol. Add 40 mL of water and phenolphthalein. Titrate with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide. Perform a blank titration, if necessary, and make the appropriate correction. Each mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 18.32 mg of saccharin (C7H5NO3S).
Acceptance criteria: 99.0% to 101.0% on the dried basis
Limit of Toluenesulfonamides: To pass the test by Chromatography.
o-Toluenesulfonamide: 10 ppm maximum.
p-Toluenesulfonamide: 10 ppm maximum.
Limit of Benzoate and Salicylate:
Sample solution: 10 mL of a hot, saturated solution of saccharin
Analysis: Add ferric chloride TS dropwise to the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria: No precipitate or violet color appears in the liquid.
Melting Range or Temperature: 226C to 230C.
Loss on Drying:
Analysis: Dry at 105C for 2 h.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.0%
Readily Carbonizable Substances:
Sample solution: 40 mg/mL in sulfuric acid [94.5% to 95.5% (w/w) of H2SO4]; maintained at 48C to 50C for 10 min.
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution has no more color than Matching Fluid A, when viewed against a white background.
Clarity of Solution: To pass the test.
Color of Solution: To pass the test.
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers. Store at room temperature.
Specifications of Saccharin BP Ph Eur Grade:
C7H5NO3S --- 183.2 --- CAS 81-07-2
Action and use: Sweetening agent.
DEFINITION
1,2-Benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one 1,1-dioxide.
Content: 99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
CHARACTERS
Appearance: White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Solubility: Sparingly soluble in boiling water and in ethanol (96 per cent), slightly soluble in cold water. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates.
IDENTIFICATION
First identification: C
Second identification: A, B, D, E
A. A saturated solution, prepared without heating, turns blue litmus paper red.
B. Melting point: 226C to 230C.
C. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry.
Comparison Saccharin CRS.
D. Mix about 10 mg with about 10 mg of resorcinol add 0.25 mL of sulfuric acid and carefully heat the mixture over a naked flame until a dark green colour is produced. Allow to cool, add 10 mL of water and dilute sodium hydroxide solution until an alkaline reaction is produced. An intense green fluorescence develops.
E. To 0.2 g add 1.5 & mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution evaporate to dryness and heat the residue carefully until it melts, avoiding carbonisation. Allow to cool, dissolve the mass in about 5 mL of water, add dilute hydrochloric acid until a weak acid reaction is produced and filter, if necessary. To the filtrate add 0.2 mL of ferric chloride solution. A violet colour develops.
TESTS
Solution S: Dissolve 5.0 g in 20 mL of a 200 g/L solution of sodium acetate and dilute to 25 mL with the same solution.
Appearance of solution: Solution S is clear and colourless.
o- and p-Toluenesulfonamide: To pass the test by Gas chromatography.
Limits:
-o-toluenesulfonamide: the ratio of its area to that of the internal standard is not greater than the corresponding ratio in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (10 ppm),
-p-toluenesulfonamide: the ratio of its area to that of the internal standard is not greater than the corresponding ratio in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (10 ppm).
Readily carbonisable substances: Dissolve 0.20 g in 5 mL of sulfuric acid and keep at 48-50C for 10 min. When viewed against a white background, the solution is not more intensely coloured than a solution prepared by mixing 0.1 mL of red primary solution, 0.1 mL of blue primary solution and 0.4 mL of yellow primary solution with 4.4 mL of water.
Loss on drying: Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105C for 2 h.
Sulfated ash: Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Specifications of Saccharin FCC Food Grade
o-Benzosulfimide; Gluside; 1,2-Benzisothiazole-3(2H)-one-1,1-dioxide
C7H5NO3S Formula wt 183.18
INS: 954 CAS: 81-07-2
DESCRIPTION
Saccharin occurs as white crystals or as a white, crystalline powder. Its solutions are acid to litmus. One gram is soluble in 290 mL of water at 25C, in 25 mL of boiling water, and in 30 mL of alcohol. It is slightly soluble in chloroform and in ether, and it is readily dissolved by dilute solutions of ammonia, solutions of alkali hydroxides, or solutions of alkali carbonates with the evolution of carbon dioxide.
Function: Nonnutritive sweetener.
REQUIREMENTS
Identification:
A. Dissolve about 100 mg of sample in 5 mL of a 1:20 solution of sodium hydroxide, evaporate the mixture to dryness and gently fuse the residue over a small flame until ammonia no longer evolves. After the residue has cooled, dissolve it in 20 mL of water, neutralize the solution with 2.7 N hydrochloric acid, and filter. Add 1 drop of ferric chloride to the filtrate. A violet color appears.
B. Mix 20 mg of sample with 40 mg of resorcinol, cautiously add 10 drops of sulfuric acid, and heat the mixture in a liquid bath at 200C for 3 min. After cooling, add 10 mL of water and an excess of 1N sodium hydroxide. A fluorescent green liquid results.
Assay: Not less than 98.0% and not more than 101.0% of C7H5NO3S after drying.
Benzoic and Salicylic Acids: Passes test.
Lead: Not more than 2 mg/kg.
Loss on Drying: Not more than 1%.
Melting Range: Between 226C and 230C.
Readily Carbonizable Substances: Passes test.
Residue on Ignition: Not more than 0.2%.
Selenium: Not more than 0.003%.
Toluenesulfonamides: Not more than 0.0025%.
Please visit Hazard Statement of Saccharin Insoluble USP NF BP Ph Eur FCC Food Grade Suppliers.
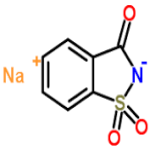
Saccharin Sodium
CAS Number: 128-44-9, 6155-57-3 & 82385-42-0 USP BP Ph Eur FCC Food Grade Suppliers Exporters, Manufacturers

Please visit Safety Data Sheet of Saccharin Sodium USP BP Ph Eur FCC Food Grade Manufacturers.
Saccharin Sodium USP Grade Specifications:
C7H4NNaO3S-2H2O --- 241.20
C7H4NNaO3S --- 205.17
1,2-Benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one, 1,1-dioxide, sodium salt, dihydrate;
1,2-Benzisothiazolin-3-one 1,1-dioxide sodium salt dihydrate CAS 6155-57-3
Anhydrous 128-44-9
DEFINITION
Saccharin Sodium contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of saccharin sodium (C7H4NNaO3S), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
IDENTIFICATION
A. Infrared Absorption
Sample: Dry at 105C to constant weight.
B. Procedure
Sample solution: 100 mg/mL
Potassium pyroantimonate solution: Dissolve 2 g of potassium pyroantimonate in 95 mL of hot water. Cool quickly and add 50 mL of a potassium hydroxide solution (50 mg/mL) and 1 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (8.5 in 100). Allow to stand for 24 h, filter, and dilute with water to 150 mL.
Analysis: To 10 mL of the Sample solution add 2 mL of 15% potassium carbonate, and heat to boiling. No precipitate is formed. Add 4 mL of Potassium pyroantimonate solution, and heat to boiling. Allow to cool in ice water and, if necessary, rub the inside of the test tube with a glass rod.
Acceptance criteria: A dense precipitate is formed.
C. Sodium salts impart an intense yellow color to a nonluminous flame.
ASSAY
Procedure
Sample solution: Dissolve 150 mg of Saccharin Sodium in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. [Note: Slight heating may be needed to dissolve the sample.]
Analysis: Titrate the Sample solution with 0.1 N perchloric acid, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 20.52 mg of saccharin sodium (C7H4NNaO3S).
Acceptance criteria: 99.0% to 101.0% on the anhydrous basis
o-Toluenesulfonamide: 10 ppm maximum.
p-Toluenesulfonamide: 10 ppm maximum.
Limit of Benzoate and Salicylate:
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL
Analysis: To 10 mL of the Sample solution add 5 drops of 6 N acetic acid, and then add 3 drops of ferric chloride.
Acceptance criteria: No precipitate or violet color appears.
Water Determination: NMT 15.0%
Readily Carbonizable Substances:
Matching fluid A: Cobaltous chloride CS, ferric chloride CS, cupric sulfate CS, and water (0.1: 0.4: 0.1: 4.4)
Sample solution: 40 mg/mL in sulfuric acid [94.5% to 95.5% (w/w) of H2SO4], maintained at 48C to 50C for 10 min.
Acceptance criteria: The Sample solution has no more color than Matching fluid A, when viewed against a white background.
Acidity or Alkalinity:
Sample solution: 100 mg/mL in carbon dioxide-free water
Analysis: To 10 mL of the Sample solution add 1 drop of phenolphthalein.
Acceptance criteria: No red or pink color is produced. Then add 1 drop of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide: a red or pink color is produced.
Clarity of Solution: To pass the test.
Color of Solution: To pass the test.
Packaging and Storage: Preserve in well-closed containers. Store at room temperature.
Specifications of Saccharin Sodium BP Ph Eur Grade
Soluble Saccharin
C7H4NNaO3S --- 205.2 --- CAS 128-44-9
Action and use: Sweetening agent.
DEFINITION
2-Sodio-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one 1,1-dioxide.
Content: 99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance). It may contain a variable quantity of water.
CHARACTERS
Appearance: White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, efflorescent in dry air.
Solubility: Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
IDENTIFICATION
First identificationiB, E.
Second identificationiA, C, D, E.
A. Melting point: 226C to 230C.
To 5 ml of solution S (see Tests) add 3 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid. A white precipitate is formed. Filter and wash with water. Dry the precipitate at 100C to 105C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry.
C. Mix about 10 mg with about 10 mg of resorcinol, add 0.25 ml of sulphuric acid and carefully heat the mixture over a naked flame until a dark green colour is produced. Allow to cool, add 10 ml of water and dilute sodium hydroxide solution until an alkaline reaction is produced. An intense green fluorescence develops.
D. To 0.2 g add 1.5 ml of dilute sodium hydroxide solution, evaporate to dryness and heat the residue carefully until it melts, avoiding carbonisation. Allow to cool, dissolve the mass in about 5 ml of water, add dilute hydrochloric acid until a weak acid reaction is produced and filter, if necessary. To the filtrate add 0.2 ml of ferric chloride solution. A violet colour develops.
E. Solution S gives reaction (a) of sodium.
TESTS
Solution S: Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water and dilute to 50.0 ml with the same solvent.
Appearance of solution: The solution is clear and colourless.
Dissolve 5.0 g in 25 ml of carbon dioxide-free water.
Acidity or alkalinity: To 10 ml of solution S add about 0.05 ml of a 10 g/l solution of PhPh in ethanol (96 per cent). The solution is not pink. Add 0.1 ml of sodium hydroxide 0.1 M. The solution becomes pink.
o- and p-Toluenesulphonamide: Gas chromatography to pass the test.
Readily carbonisable substances: Dissolve 0.20 g in 5 ml of sulphuric acid and keep at 48C to 50C for 10 min. When viewed against a white background, the solution is not more intensely coloured than a solution prepared by mixing 0.1 ml of red primary solution, 0.1 ml of blue primary solution and 0.4 ml of yellow primary solution with 4.4 ml of water.
Heavy metals: Maximum 20 ppm.
Water: Maximum 15.0 per cent, determined on 0.200 g.
ASSAY
Dissolve 0.150 g in 50 ml of anhydrous acetic acid, with slight heating if necessary. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically. Carry out a blank titration. 1 ml of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 20.52 mg of C7H4NNaO3S.
In an airtight container.
Specifications of Sodium Saccharin FCC Food Grade
1,2-Benzisothiazole-3(2H)-one 1,1-Dioxide Sodium Salt;
Sodium o-Benzosulfimide; Soluble Saccharin
C7H4NNaO3S·2H2O --- Formula weight 241.19
INS: 954 CAS: 128-44-9
DESCRIPTION
Sodium Saccharin occurs as white crystals or as a white, crystalline powder. In powdered form, it effloresces to the extent that it usually contains only about one-third the amount of water indicated in its molecular formula. One gram is soluble in 1.5 mL of water and in about 50 mL of alcohol.
Function: Nonnutritive sweetener.
Identification:
A. Dissolve about 100 mg of sample in 5 mL of a 1:20 solution of sodium hydroxide, evaporate to dryness, and gently fuse the residue over a small flame until ammonia no longer evolves. After the residue has cooled, dissolve it in 20 mL of water, neutralize the solution with 2.7 N hydrochloric acid, and filter. Add 1 drop of ferric chloride to the filtrate. A violet color appears.
B. Mix 20 mg of sample with 40 mg of resorcinol, cautiously add 10 drops of sulfuric acid, and heat the mixture in a liquid bath at 200C for 3 min. After cooling, add 10 mL of water and an excess of 1 N sodium hydroxide. A fluorescent green liquid results.
C. The residue obtained by igniting a 2-g sample gives positive tests for Sodium.
D. Add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid to 10 mL of a 1:10 aqueous solution. A crystalline precipitate of saccharin forms. Wash the precipitate well with cold water, and dry at 105C for 2 h. The saccharin thus obtained melts between 226C and 230C.
Assay: Not less than 98.0% and not more than 101.0% of C7H4NNaO3S, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Alkalinity: Passes test.
Benzoate and Salicylate: Passes test.
Lead: Not more than 2 mg/kg.
Readily Carbonizable: Substances Passes test.
Selenium: Not more than 0.003%.
Toluenesulfonamides: Not more than 0.0025%.
Water: Not more than 15.0%.
Please visit Hazard Statement of Saccharin Sodium USP BP Ph Eur FCC Food Grade Suppliers.
Saccharin Insoluble CAS Number 81-07-2 & Saccharin Sodium CAS Number 128-44-9, 6155-57-3 & 82385-42-0 Supplier Exporter, Manufacturer:
Annie Chemie P Ltd
Mumbai 4000010, INDIA
With Agents and offices in UAE, USA, Europe.
e-mail: info@anniechemie.com
Copyright and Usual Disclaimer is Applicable.
June 1, 2025
Exporters to USA, Canada, UK, Europe, UAE, Nigeria, Algeria, Turkey, Mexico, Brazil, Chile, Argentina, Australia, Dubai etc.
Perfection is made up of small things and that is a big thing.
